Conservation of Energy
Goals
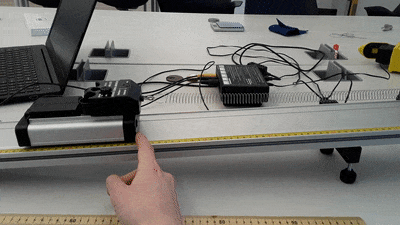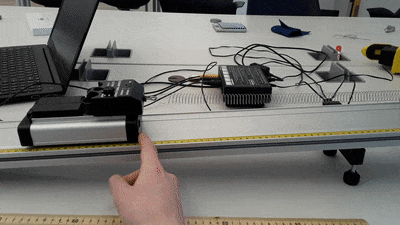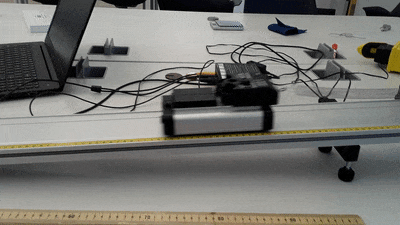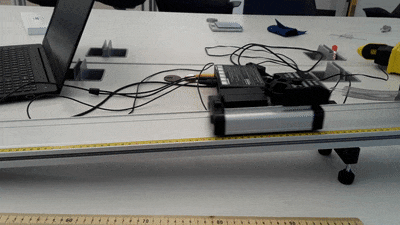
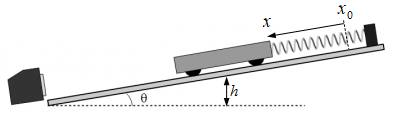
- Find the spring constant and zero-force position of the spring as shown in the diagram below.
- Compare the kinetic and potential energy of a cart attached to a spring on an inclined track as it oscillates up and down the track
Resources
- Cart track with end bumper, adjustable legs, and angle indicator
- Collision cart with weights
- Spring
- Motion sensor
- Force sensor
- ScienceWorkshop interface and DataStudio software
- Datastudio setup file energycons3.ds
There are many different forms of energy. Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy of an object in a gravitational field, and the elastic energy stored in a spring. Energy has the property that it is always conserved. It can be changed into other forms of energy, and sometimes this change is not easily reversible – as in the case of conversion to thermal energy due to friction – but energy can never be truly “lost”.
The cart in this experiment has kinetic energy KE=\tfrac{1}{2}mv^2 It also has potential energy at each point due to its height above the table and the amount by which the spring is stretched.
Potential energy in general is equal to the amount of work a force would do to move an object to its current position from a reference point. The restoring force that a spring exerts when its end is stretched or compressed to a position x, where x_0 is the location of the end of the spring in its “relaxed” state, can be modeled as F=-k(x-x_0) where k is the spring stiffness constant. A stretched or compressed spring has elastic potential energy PE_{elastic}=\tfrac{1}{2}k (x-x_0)^2
The gravitational potentional energy of the cart relative to its lowest point h=0 is simply PE_{gravity}=mgh
Method
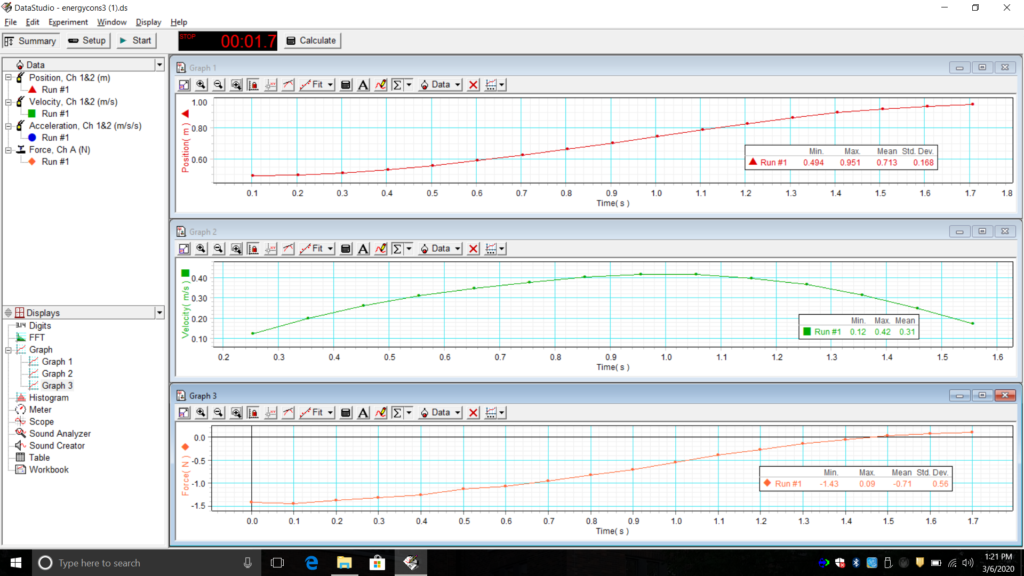
Set up the cart, track, and sensors as shown above. Pull the cart down the track a short distance and release it. If you pull the cart down too far, the spring will bunch up in a way that doesn’t follow the linear force relationship given above. Record data from the time the cart is released until it reaches its highest point.
Analysis Questions
- Is the mechanical energy of the cart conserved in this experiment?
- Is the total energy conserved? Justify your conclusion using your data and uncertainty estimates/calculations.