Diffraction Patterns
Objectives
- Measure the spacing of light and dark fringes in single slit and double slit interference patterns.
- Calculate the width of the slits based on the spacing of the fringes in the diffraction patterns.
Resources
- Optical bench
- Green diode laser
- mounted single- and multiple-slit diffraction masks
- mounted screen
Background
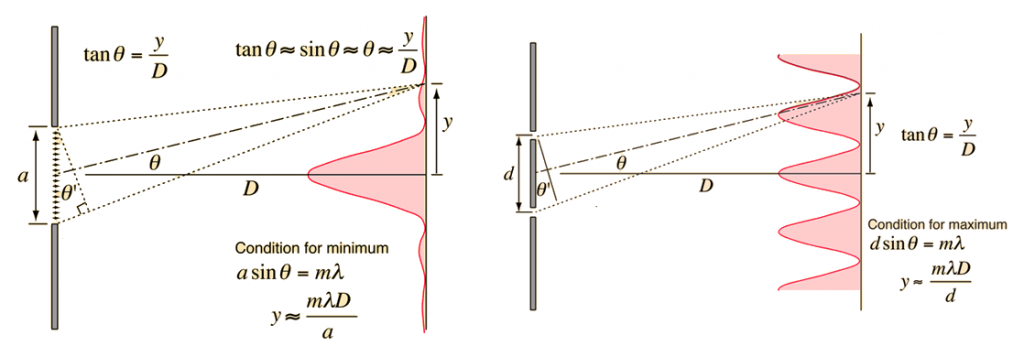
When waves of any type pass through each other, their amplitudes add together at points where they overlap. They can cancel each other out or enhance each other at different points, depending on their relative phase and amplitude at a given position. Shining laser light at a small opening that is comparable in size to the wavelength of the light allows the interference of light to be easily observed. Light from the opening will radiate equally in all directions and interfere with itself.
If light of wavelength \lambda is shone at a single slit of width a, the light will produce dark fringes at locations given by a\sin\theta=m\lambda where m=0,1,2,\cdots denotes the m^{th} dark fringe of the interference pattern. If there are multiple slits spaced a distance d apart, each slit will produce an overlapping interference pattern with bright fringes at locations given by d\sin\theta=m\lambda.